Key Takeaways
- Air conditioning relies mainly on fossil-fuel-generated electricity, contributing to climate change.
- ACs use HFCs as refrigerants, which are potent greenhouse gases.
- Switching to energy-efficient units and eco-friendly refrigerants can reduce environmental impact.
When it comes to maintaining your home’s climate, it has never been more essential to seek out sustainable, green air conditioning options.
Traditional air conditioners may cool effectively, but they consume significant energy and contribute to carbon emissions. While fully eco-friendly air conditioning (that is, carbon-neutral or powered by 100% renewable energy) isn’t here yet, new technologies are helping move toward more sustainable options.
You can still reduce the adverse environmental impact by opting for environmentally safe air conditioners; let’s explore all the options in this blog.
Air Conditioning Usage & Environmental Concerns
As weather patterns shift around the year, with longer heat waves and high temperatures lasting into the fall, air conditioning has become essential for keeping homes cool and comfortable. However, as demand increases, high energy consumption is driving up greenhouse gas emissions.
Air conditioning accounts for approximately 19% of the electricity consumption in the U.S. A substantial share of this electricity is generated by fossil-fuel combustion, which emits significant carbon dioxide, a major contributor to global warming.
Additionally, as air conditioning demand grows worldwide, electricity grids are under greater strain. As heat waves become more frequent and severe across U.S. cities, this pressure on power grids is expected to continue during peak summer months, increasing the risk of energy demand spikes and grid instability.
R-410A vs. R-22 Freon
Another major problem with air conditioners is that they use hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) as refrigerants, which are potent greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere and are among the fastest-rising contributors to global pollution. By 2030, emissions from cooling appliances, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, are expected to increase further.
Most air conditioners manufactured in the last five years use R-410A, a refrigerant that is less harmful to the environment than its predecessor, R-22 (Freon). R-22 was known to deplete the ozone layer, which shields Earth from harmful UV radiation. In the U.S., production and import of new R-22 ended on January 1, 2020, but reclaimed/recycled R-22 can still be used to service existing equipment.
Air conditioners keep your home comfortable, but they also contribute to global warming. As more people use air conditioning, up to three-quarters of the world’s population may encounter deadly heat and humidity by the end of the century.
Green HVAC: How to Make Your AC More Eco-Friendly
Here are some ways to make your air conditioning more eco-friendly and environmentally clean:
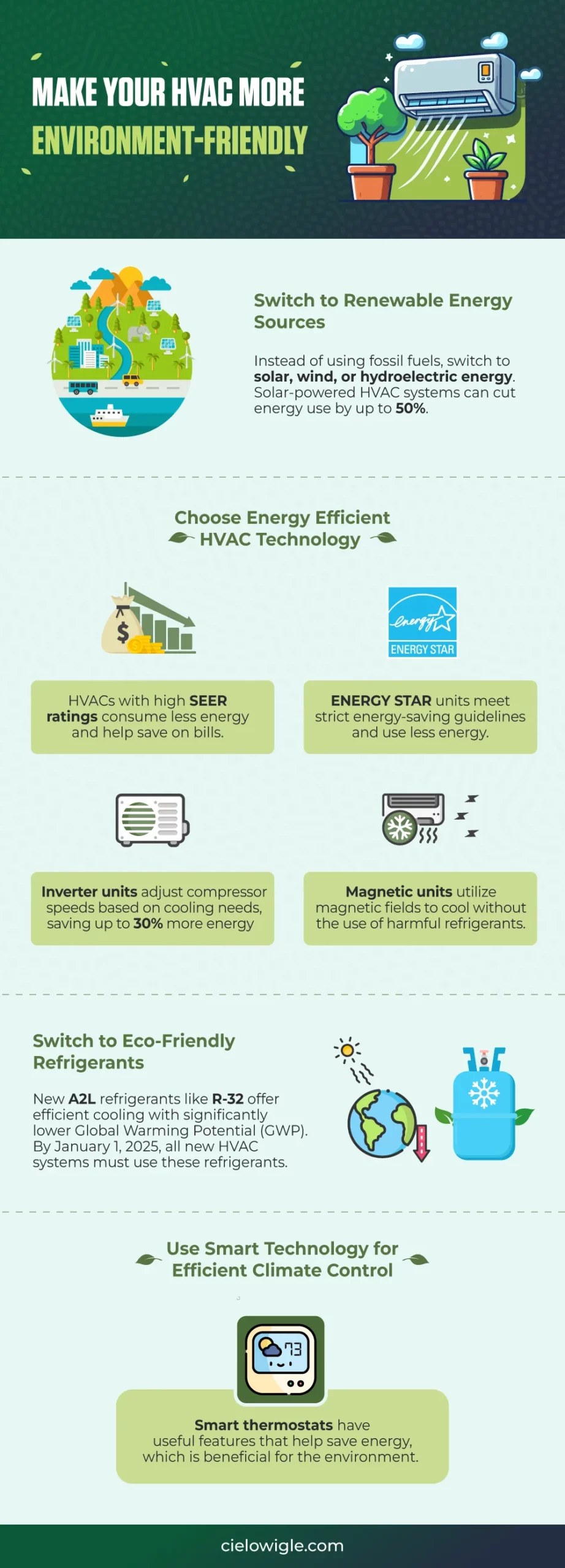
-
Reliance on Renewable Energy
Using renewable energy to power air conditioning is a significant step in making cooling systems more sustainable. Instead of using fossil fuels, air conditioners can be operated using solar, wind, or hydroelectric energy. This helps to reduce the amount of pollution that contributes to climate change.
Solar-powered air conditioning is an excellent example. It absorbs energy from the sun to cool your home. This means you won’t be using as much electricity from the power grid, which could reduce your energy use by up to 50%, depending on where you live. While you may still require some power from the grid, the huge reduction in usage can result in significant savings on your cooling expenses.
-
Choose Energy-Efficient HVAC Technology
When purchasing an air conditioner, look for one with a high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating. A higher SEER rating means the system uses less energy to deliver the same level of cooling, which can lower electricity bills and reduce environmental impact.
As of January 1, 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has transitioned from SEER to SEER2. This update introduced revised testing procedures designed to better reflect real-world operating conditions, providing a more accurate measure of system efficiency.
Additionally, look for air conditioners with the ENERGY STAR label. It means they comply with the US government’s energy-saving standards. These models save energy and emit fewer greenhouse gases, making them better for the environment.
Another great option is an inverter air conditioner. These include smart compressors that can speed up or slow down according to how cool your home needs to be, saving up to 30% more energy than regular models that only operate at one pace.
Magnetic refrigeration is a new technology that rethinks convehttps://cielowigle.com/blog/inverter-air-conditioner/ntional cooling systems. Andy Shu, an HVAC specialist at Zap Fixers, explains, “Magnetic cooling systems utilize magnetic fields to cool without the use of harmful chemical refrigerants.”
Though magnetic refrigeration shows great potential, it is still under development. However, it’s a technology worth watching in the next five to ten years.
-
Adoption of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants
Switching to less hazardous refrigerants is an important step in making air conditioning more environmentally friendly. Common refrigerants, known as HFCs, have high Global Warming Potential (GWP). Mehdi Khachani, CEO of Sunny Bliss Plumbing & Air Conditioning, says, “Traditional air conditioning systems, which rely on high-GWP refrigerants, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.”
A newer variant, R-32, is gaining popularity because it performs well and has a significantly lower GWP. This means it is better at cooling while consuming approximately 10% less electricity than previous refrigerants such as R-22. Furthermore, R-32 has a lower GWP, about one-third of that of the most common refrigerants, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has mandated that by January 1, 2025, all new residential and light commercial air conditioners and heat pumps utilize A2L-family refrigerants such as R-32. “Transitioning to these green technologies on a larger scale could make a substantial difference in reducing global carbon emissions,” Khachani adds.
Another next-generation A2L refrigerant being adopted is R-454B, also known as Puron Advance. It is a blended refrigerant R-32, a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC), and R-1234yf, a hydrofluoroolefin (HFO). R-454B has an Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) of zero and a low Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 466, which is 78% lower than R-410A (GWP 2088). It is primarily used in new air conditioners and heat pumps to help meet stricter environmental regulations.
-
Smart Technology for Efficient Climate Control
Smart mini-split thermostats and smart thermostats for central HVAC systems have useful features that help save energy, which is beneficial for the environment. One convenient feature is the ability to adjust your home’s temperature from anywhere using your phone. If your plans change and you are not home, you can reduce the AC to save energy. You may also control the thermostat to adjust temperatures during the day, such as raising it when you’re away, to reduce the amount of time your air conditioner runs and how much electricity it consumes.
Equip your HVAC system with smart features and achieve the perfect balance between comfort & savings.
Learn more
These smart home climate-control products also provide detailed information on your air conditioning usage. This shows where you can save more energy and reduce your carbon footprint.
Expert Tips for a Greener Air Conditioning System
Here’s how you can adjust your daily routines and maintenance practices for air conditioning to be more environmentally friendly and reduce energy wastage.
-
Thermostat Setback Strategy
To save money on heating and cooling, consider lowering your thermostat by 7-10 degrees when you are not home. According to the Department of Energy, making this simple change, called the thermostat setback strategy, can help you save approximately 10% on your energy bills.
-
Choosing the Ideal Temperature Settings
The best temperature to set your thermostat when you are awake and at home is 68 degrees (in the winter) and 78 degrees (in the summer). This temperature keeps you comfortable while conserving electricity, benefiting both your budget and the environment.
-
Clean Your Filters
Keeping your air filters clean is essential for efficient energy use. When filters become clogged with dust and debris, the system must work harder to pull air through, increasing energy consumption.
-
Enhance Home Insulation
Improve the insulation in your home and seal any gaps to save energy on heating and cooling. Proper insulation in your attic, walls, and floors helps maintain a consistent temperature inside, allowing your HVAC system to work less hard. Sealing cracks or gaps around doors, windows, and ducts prevents air from escaping and makes your home more energy efficient.
-
Regular HVAC Maintenance
Maintaining your HVAC system on a regular basis is essential for energy savings. Simple actions, including cleaning filters, inspecting ducts, and tuning up components, help your system function more efficiently and save energy. When your HVAC system is in good condition, it runs more smoothly, lasts longer, and you won’t have to worry about costly repairs later.
-
Replace or Repair
Consider whether it is best to replace your old HVAC unit rather than spend money on repairs that may result in higher long-term costs. Purchasing a new, energy-efficient system is sometimes a better, more environmentally friendly option than repeatedly repairing an outdated system.
Paving the Way for a Sustainable Future
Switching to green air conditioning is beneficial not just for your home’s energy use but also for reducing your carbon footprint. You can implement energy-saving measures, use eco-friendly refrigerants ,and smart HVAC controls to reduce your energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. These adjustments benefit the environment while also saving you money and making your home more comfortable over time.








