Key Takeaways
- Cold-climate heat pumps efficiently extract heat from outdoor air even in freezing conditions.
- They have features like variable-speed compressors and cold-weather refrigerants to aid in heat extraction.
- Mitsubishi, Lennox, Daikin, and Fujitsu have introduced cold-climate heat pumps.
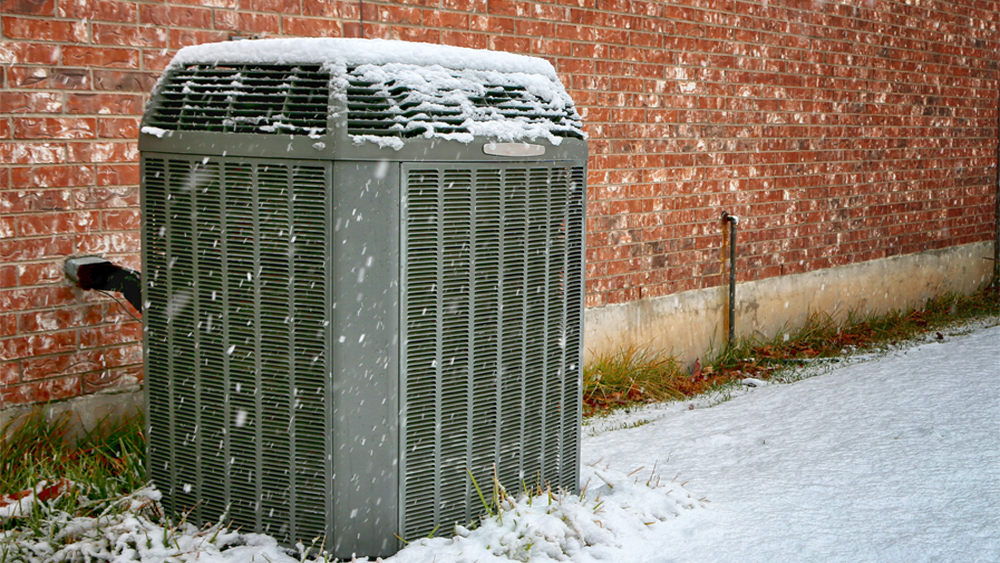
Heat pumps are gaining momentum in the US as a go-to solution for residential heating and cooling. They are not only highly efficient but also a sustainable alternative to traditional HVAC systems. Heat pumps extract heat from the air or ground, meaning they don’t burn fossil fuels and emit environmentally harmful greenhouse gases. However, there’s one concern associated with the heat pumps – do they provide a reliable heating option in cold weather?
Recent research by Oxford University and the Regulatory Assistance Project has dispelled the common misconception that heat pumps are only suitable for milder climates. In fact, they have been found to be more than twice as efficient as fossil fuel heating systems, even in temperatures as low as -22F.
This blog will explore everything you need to know about cold-climate heat pumps, from how they work to their unique features and the best options on the market to keep you comfortably warm when the winter chill hits.
How Do Cold-Climate Heat Pumps Work?
Cold-climate heat pumps are an environmentally friendly option and operate similarly to your standard heat pumps. They use refrigerant-filled coils to transfer heat from outside to your home. Even when the weather is cold, heat is still present in the outdoor air, and that’s why heat exchange occurs.
In residential settings, air-source heat pumps are mostly used. They extract heat from the outdoor air using a heat exchanger. This air is warm enough to cause the refrigerant to change its state from liquid to gas. The gaseous refrigerant is moved to the compressor, which pressurizes and heats it further. After this, the refrigerant releases its heat, and the warm air is distributed throughout your home using fans and ducts or an indoor unit in case of a ductless heat pump.
Cold-Climate Heat Pump Features That Maximize Efficiency
Cold-climate heating systems can operate at up to 400% efficiency, which means they produce four times more energy than they consume. It’s true that as the temperature drops, the heat pump has to work harder to provide heat. However, these units have various features and components that help them perform effectively even in the most extreme conditions.
- Variable-Speed Compressor
When it comes to heat pumps in cold climates, the variable-speed compressor is the standout feature that sets them apart. Powered by an inverter, this advanced technology can be useful in any climate, but it’s particularly advantageous in regions where temperatures dip below freezing.
One-speed compressors are more prone to erratic climate swings caused by frequent on/off cycling. Compared to that, a variable-speed system maintains a more consistent temperature and humidity level in every season.
The operation of a variable speed compressor can be compared to a car accelerator. Single-speed heat pumps can only go either 0 or 100 mph, meaning they’re either on or off. In contrast, variable-speed heat pumps can operate at many speeds, making them incredibly efficient.
These systems can run at high speeds during extreme weather conditions but reduce speed during milder days for optimal energy use. The flexibility of variable-speed systems translates to energy savings, just like your car mileage is better when you drive at a steady pace.
- Flash or Vapor Injection
Standard heat pumps can lose their heating capacity as outdoor temperatures drop, leaving your home uncomfortably cold. However, cold-climate heat pumps have found a way to boost their performance in these conditions.
By opening up a shortcut in their refrigerant loops, the heat pump can better handle the cold weather. A small amount of refrigerant is allowed to pass the expansion valve before it is re-injected at a high temperature back into the compressor. While peak efficiency drops slightly, the overall efficiency is improved using this technology.
- Cold-Weather Refrigerants
Cold-weather refrigerants, also referred to as low-temperature or winter-grade refrigerants, have a lower boiling point than traditional refrigerants. This allows the refrigerant to continue flowing through the system at low ambient temperatures.
By using a cold-weather refrigerant, a heat pump can draw more heat energy from the cold air. Cold-climate heat pumps also have electronic expansion valves that regulate the flow of refrigerant.
- Sensors and Controls
Cold-climate heat pumps have various sensors and advanced controls to match the refrigerant flow and volume to the compressor and fan speed. This ensures that the unit does not damage itself while working at lower temperatures.
- High-Efficiency Ratings
The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) determines the energy efficiency of a heating system. It is a measure of how much heating output you get for the amount of electricity consumed during a heating season. A higher HSPF value means the heat pump is more efficient, producing more heat while using less energy. Cold-climate heat pumps deliver an HSPF of 10 or greater. They excel at extracting heat from the outdoor air, ensuring an ideal climate for your home.
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a metric that measures the efficiency of a heat pump at a specific time rather than over a whole heating season. Cold-climate heat pumps can achieve COP ranging from two to three at 30-40F. They can maintain a COP of more than one at even low temperatures.
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) determines how well your heat pump cools. It measures your unit’s cooling output divided by the energy it uses during the entire summer. SEER ratings for cold-climate heat pumps can go up to 28.
Types of Heat Pumps for Cold Climate
Two options that stand out for their reliability and efficiency in cold weather are geothermal heat pumps and cold-climate air source heat pumps.
Related: Types of Heat Pumps: What Are They, How Do They Work, and Which Is the Best for You?
-
Cold-Climate Air-Source Heat Pump
Air-source heat pumps have come a long way in recent years when it comes to heating homes in cold climates. Cold-climate air source heat pumps now feature variable-speed, inverter-driven compressor technology and improved defrost-cycle controls that weren’t available just a decade ago.
Cold-climate heat pumps come in both ducted and ductless units. If your home already has ductwork, then opting for a ducted heat pump may be the best fit for you. However, if you don’t have any existing ductwork, then a ductless system, also known as a mini-split, is an excellent choice.
The two options differ in how they deliver heat and cooling, but both are equally capable of providing effective cold-weather performance.
Related: Forced Air Heating – How Does It Work?
-
Geothermal Heat Pump
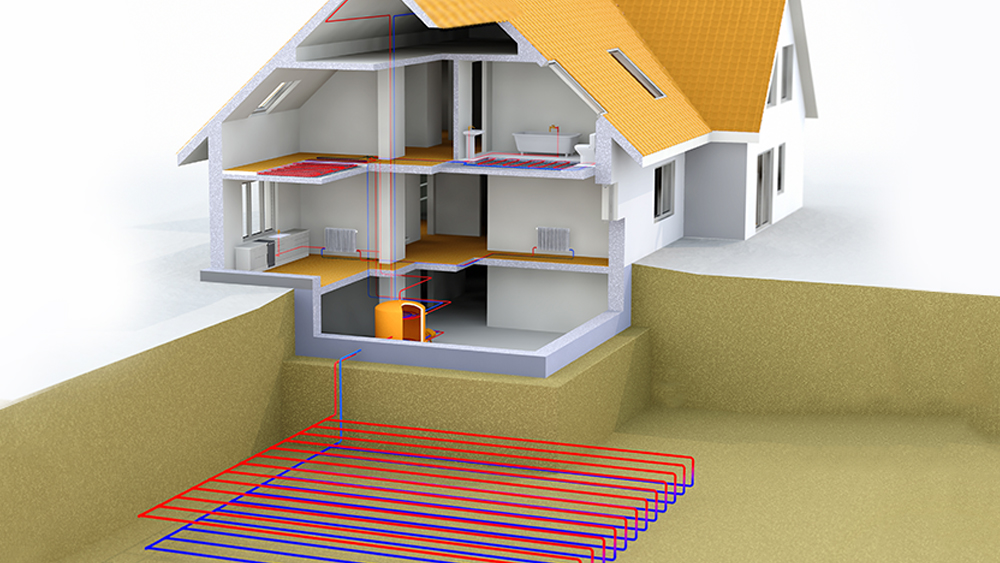
Geothermal heat pumps are a highly efficient way to heat and cool your home by utilizing the stable temperature of the earth. The temperature remains constant 10 feet below the earth and is not influenced by fluctuations that happen above ground. By using loops buried underground or submerged in water, these systems are able to exchange heat effectively.
However, it is worth noting that the installation of geothermal systems can be space-intensive and costly due to the excavation required. Despite these initial expenses, many eco-conscious homeowners with sufficient outdoor space choose geothermal heat pumps for their long-term energy savings and high efficiency.
How to Make Cold Climate Heat Pumps Smart?

To make the most of your heat pump, consider pairing it with a smart thermostat or a mini-split thermostat in case of a ductless heat pump. These devices allow you to have full control of your system from anywhere in the world using your phone. They have various features that help you maintain your ideal home climate regardless of how cold it’s outside.
With smart scheduling, you can easily tailor your heating preferences around your daily routine. Once programmed, your thermostat takes over, seamlessly implementing your settings to keep your indoor climate comfortable throughout the day.
Equip your HVAC system with smart features and achieve the perfect balance between comfort & savings.
Learn more
Furthermore, using the geofencing mode, these devices automatically adjust themselves when you are away from your home, minimizing energy consumption and reducing your monthly utility bills. When you return home, your living space is brought back to your desired comfort level without any additional effort on your part.
To prevent your pipes from freezing up in cold weather, you can use smart mini-split thermostats such as Cielo Breez to run your mini-split on freeze protection (FP) mode. This mode operates your unit in a low power mode of around 46F, ensuring your home stays above freezing while reducing any unnecessary energy consumption.
Your best choice to make any mini-split, window,
or portable AC smart. Enhance your comfort and savings.

Best Cold-Climate Heat Pumps
Mitsubishi, Lennox, Daikin, and Fujitsu are some of the top brands that have introduced heat pumps specially designed for cold climates.
1. Mitsubishi Hyper-Heating or H2i M and P-Series
Mitsubishi hyper-heating M series includes mini-split heat pumps that deliver consistent heating power even in extremely cold temperatures. They come with a heating capacity that remains fully effective at 5F and still produces useful heat even at -13F.
The P series includes residential and light commercial units with flash injection technology. This advanced tech allows for outstanding heating capacity even in frigid temperatures as low as 5F. The heating operation range extends to -13F. The fash Injection circuit not only enhances start-up and recovery from defrosting but also improves the efficiency of the defrost operation control. These technologies allow the temperature to reach the desired setting quickly and also help to maintain them effectively.
Mitsubishi cold-climate heat pumps offer HSPF ratings ranging up to 13.3 and SEER up to 28.
2. Fujitsu AOU Cold-Climate Heat Pump Series
When it comes to cold-climate heat pumps, the Fujitsu AOU series is a top contender. With variable-speed models that can produce anywhere from 75-95% as much heat at 5F as they do at 47F, there’s no question that these pumps are built to withstand colder climates. In fact, they’re rated to work down to -10F. In terms of energy efficiency, Fujitsu cold-climate heat pumps range in HSPF ratings from 9.5 to 11.5 and SEER ratings from 16.5 to 20.
3. Daikin Fit and Aurora Series
The Daikin’s Fit and Aurora cold-climate heat pumps are equipped with exceptional cold-climate specifications. The Fit units are capable of operating at full heating capacity even at temperatures as low as 5F and have an impressive working capacity down to -4F. It has a variable-speed swing compressor and an ambient temperature sensor that allows it to operate efficiently.
The Aurora series goes even further, with the ability to operate down to -13F.
The Aurora and Fit lines boast impressive HSPF ratings ranging from 9 to 11 and SEER ratings between 16 and 18.5.
4. Lennox SL25XPV Heat Pump
The Lennox cold-climate heat pump stands out as a leading choice for those seeking a highly efficient heating solution. It is an ENERGY STAR-certified cold-climate heat pump with high-efficiency ratings – HSPF 11.8 and SEER 24.
Moreover, it is equipped with Lennox’s revolutionary Quantum Coil, which is an aluminum alloy designed to withstand the toughest of conditions and preserve performance in cold weather.
Wrapping Up
As temperatures drop in colder regions, heating your home can become an expensive and often difficult task. This is where cold-climate heat pumps come in. These specialized HVAC systems are designed to provide efficient heating even in sub-zero temperatures. They operate by extracting heat from the surrounding air and transferring it indoors, which is much more efficient than traditional heating methods. Plus, they can also function as air conditioners, providing year-round comfort for your home. With advancements in technology, these systems have become increasingly viable options for homeowners seeking an efficient and eco-friendly heating solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Can You Save With Cold-Climate Heat Pumps?
According to the Department of Energy, cold-climate heat pumps provide high-efficiency heating and can help you save as much as $500 a year on your energy bills.
Determining the exact amount of money you can save depends on various factors:
- Cold-climate heat pumps offer impressive efficiency, but unlocking their full potential requires proper installation.
- If there are air leaks in your home and you haven't upgraded your home insulation in a while, it can impact your energy bills.
- Ductless heat pumps transfer heat energy directly to where it’s needed, eliminating heat loss associated with ductwork. This makes them more efficient than ducted units.
- Many homeowners in cold climates rely on inefficient fuels like fuel oil and propane to heat their homes. So, if you are a resident of a cold state such as Maine, Ohio, or New York, you can significantly save on your heating bills by switching to a high HSPF unit.
- Energy incentive programs and rebates can help cut down on the installation costs of cold-climate heat pumps.
What State Residents Should Get Cold-Climate Heat Pumps?
Cold-climate heat pumps are particularly beneficial for those residing in states with harsh winter climates, such as Minnesota, Minneapolis, Maine, Alaska, and Michigan.
These models are specifically designed to tackle the challenges of sub-zero temperatures, ensuring that your home stays warm and comfortable even during the coldest months of the year. However, if you live in a state with milder winters, such as those in the southern US, a standard heat pump may be all you need.
Does Heat Pump Sizing Matter?
Choosing the right heat pump size for your home is crucial for optimal heating and cooling. A heat pump that is too small will need help to maintain your desired temperature, resulting in constant operation, wear and tear, and higher energy costs.
On the other hand, a heat pump that is too large will cycle on and off too frequently, causing temperature fluctuations and potential damage to the system. Find the perfect fit to maximize efficiency and comfort.
Do You Need a Backup Heating System?
Even in areas of the United States that do not experience harsh winters, many single-speed heat pumps are paired with a backup heating system for those occasional below-freezing temperature dips.
However, you may not need a backup system if you opt for an advanced variable-speed heat pump that is designed for cold climates.
Still, if you are looking to enhance your comfort in temperatures below freezing, you can opt for a hybrid heat pump system. It is a combination of a heat pump with a gas-powered furnace. Another hybrid option is an electric strip, which is a backup heating setup built inside the heat pump air handler.
During mild weather, the heat pump operates as usual while seamlessly switching to the backup heating system during freezing spells.








